Home \ International \ Robbins unveils Largest Hard Rock TBM in the U.S. at Mill Creek
Robbins unveils Largest Hard Rock TBM in the U.S. at Mill Creek
14/01/2020
Pubblicato da Redazione
Adaptable machine will begin bore at 11.6 m then size down to 9.9 m
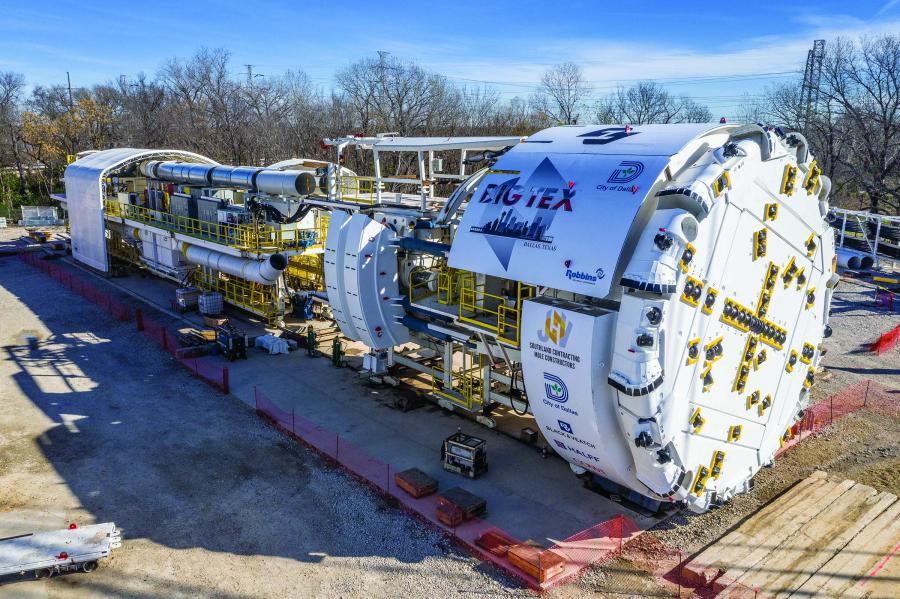
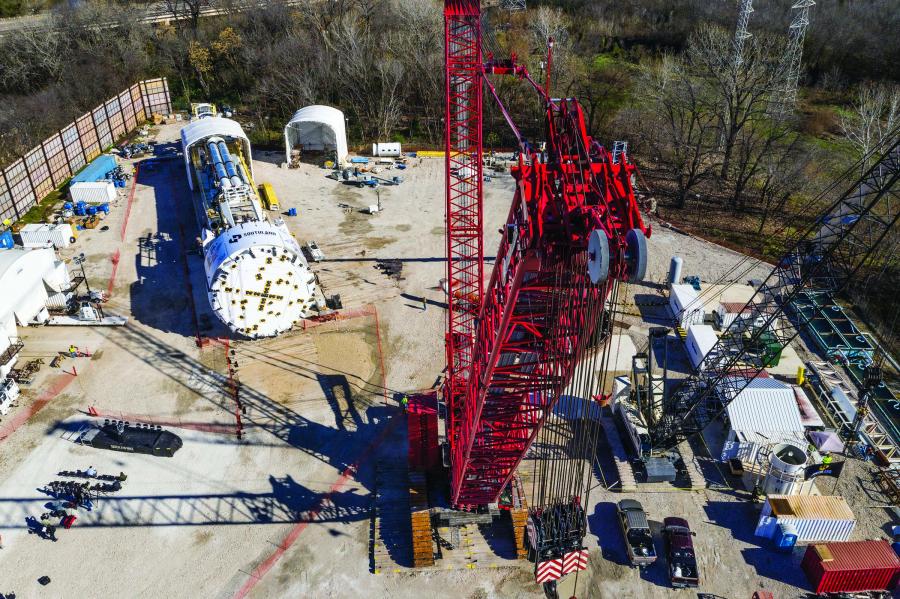
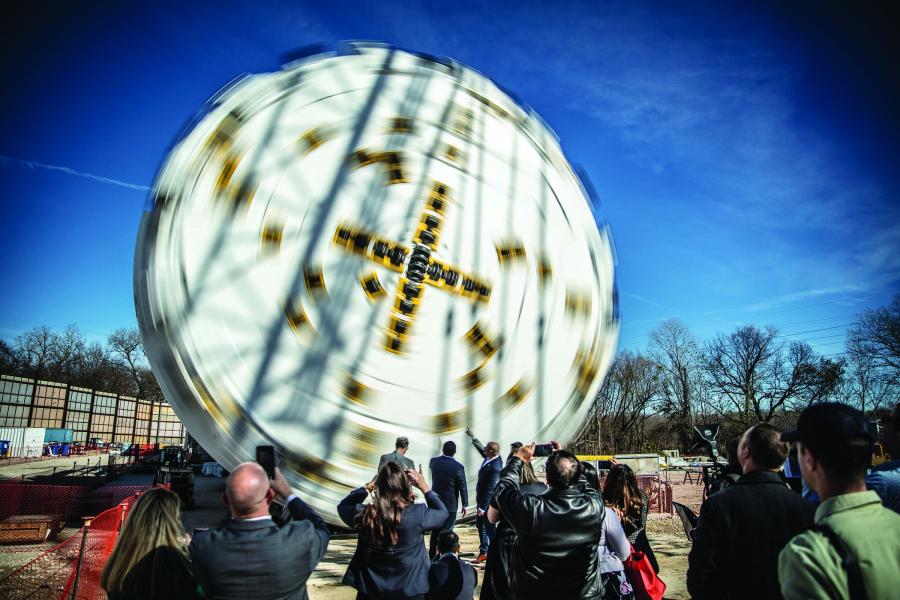
In December 2019, the City of Dallas, Texas, USA unveiled the largest hard rock TBM ever to bore in the U.S. The 11.6 m (38.1 ft) diameter Robbins Main Beam TBM will excavate the 8 km (5 mi) Mill Creek Drainage Relief tunnel, and its size is not its only distinction. The adaptable machine will change size partway through the bore, to a more compact 9.9 m (32.5 ft).
The unique Robbins TBM will be used to dig a tunnel designed to provide 100-year flood protection for east and southeast Dallas, areas affected in recent years by severe storms. The tunnel will protect 2,200 commercial and residential properties, including Baylor Medical Center. The current drainage system in these areas was constructed 50 to 70 years ago, and only provides two to five years of flood protection. “The completion of the TBM assembly marks a major milestone in the Mill Creek Tunnel Project,” said Council Member Lee Kleinman, chair of the Transportation and Infrastructure Committee for the City of Dallas. “I’m thrilled to see this type of engineering marvel happening right here in Dallas.”
The dual-diameter aspect of the Robbins TBM will be a first-of-its-kind conversion process. The contractor, Southland/Mole Joint Venture (SMJV), will make the conversion underground about 2.8 km (1.8 mi) into the bore. The two diameters are needed as the upstream section of the tunnel is designed with a circular cross section and peak flow rate of 42 m3/sec (15,000 ft3/sec), while the downstream 2.8 km (1.8 mi) portion has a higher peak flow of 565 m3/sec (20,000 ft3/sec) and was initially designed as a horseshoe cross section. Using the TBM for the entire tunnel is less time consuming and costly. “Robbins and SMJV are working closely to create the safest and most efficient sequence for completing this conversion within the limits of the bore. The City of Dallas (Owner) and our Project Team are very excited to embark on this unique challenge,” said Nick Jencopale, Project Manager for Southland Holdings.
The Robbins TBM, named “Big Tex” with permission of the State Fair of Texas, has been designed with a specialized cutterhead including removable spacers and adjustable bucket lips to convert to a smaller diameter. The TBM will first complete its 11.6 m (38.1 ft) diameter section of the alignment, then back up about 21 m (75 ft) to a transition area for the conversion, which is expected to take six to eight weeks.
As the TBM bores, it will pass through Austin Chalk between 12 to 30 MPa (1,800 to 4,400 at depths from 31 to 46 m (100 to 150 ft) below the city. The route is potentially gassy, so probe drilling is mandatory throughout the project. Crews will utilize ground support including eight 3.9 m (13 ft) long rock bolts every 1.5m (5 ft) with wire mesh and channel straps as needed. The finished tunnel will be lined with a 380 mm (15 in) thick cast-in-place concrete lining.
“Big Tex will work 24 hours a day to excavate the tunnel with crews ranging in size depending on activities,” said Rachel Sackett, marketing and communications director for Southland Holdings. Based on previous work through similar geology, the project team expects TBM excavation to progress rapidly to an average of 25m (80 ft) per day, allowing the project to be completed on schedule in 2023.

Ultime notizie di OnSite News

Earthmoving Machinery
25/11/2024
Prinoth Unveils Expanded Production Facility in Granby, Canada
Prinoth held an event to announce the official opening of it...

Logistics
22/11/2024
Sarens acquires additional SCHEUERLE SPMT K24 modules
renowned for its expertise in crane rental services, heavy l...
Equipments
21/11/2024
SITECH partners with Royal Engineers to create poppy and demonstrate tech offering
The demostration involved creating a ground-level poppy desi...

Earthmoving Machinery
20/11/2024
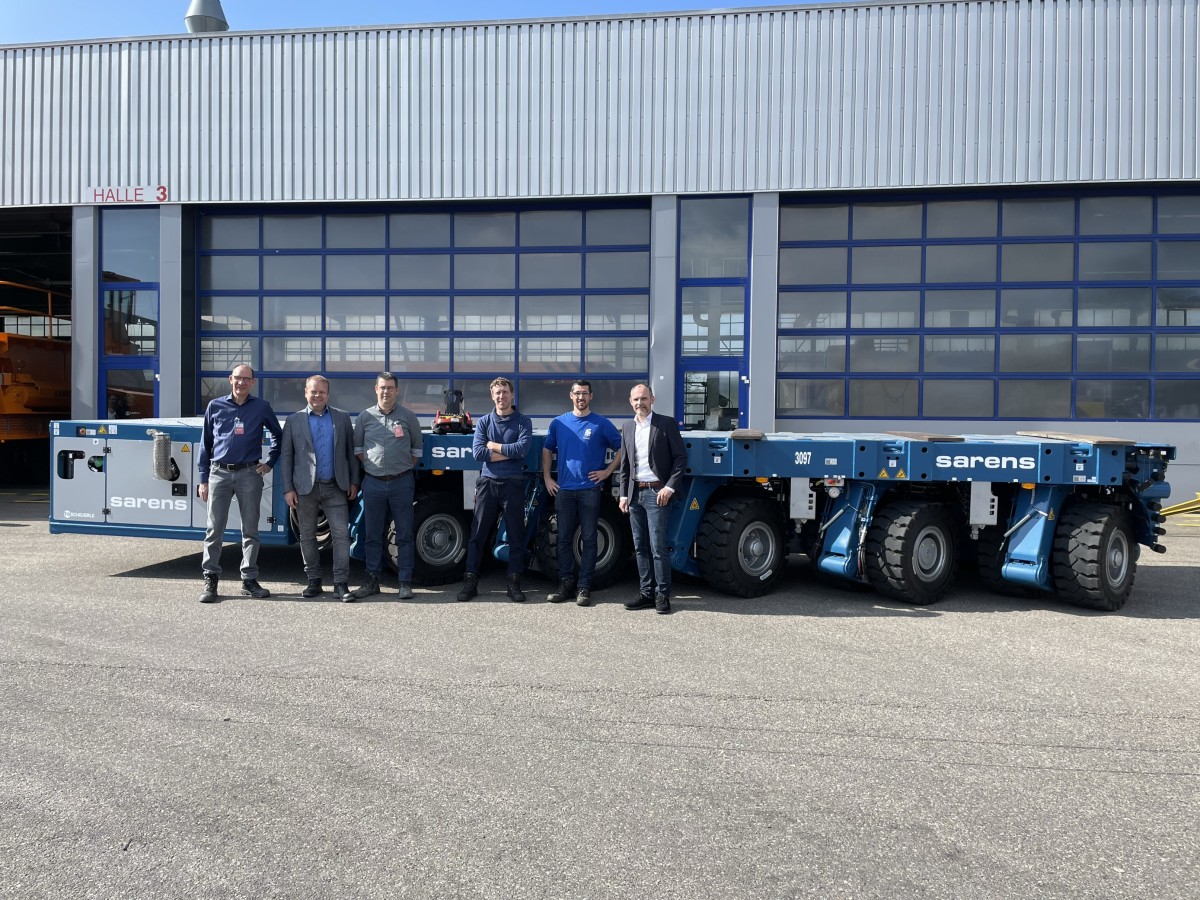
Strong and stable RA30 trucks carry the weight at New Caledonian mine
Three Rokbak RA30 trucks are delivering exceptional durabili...

Lifting
20/11/2024
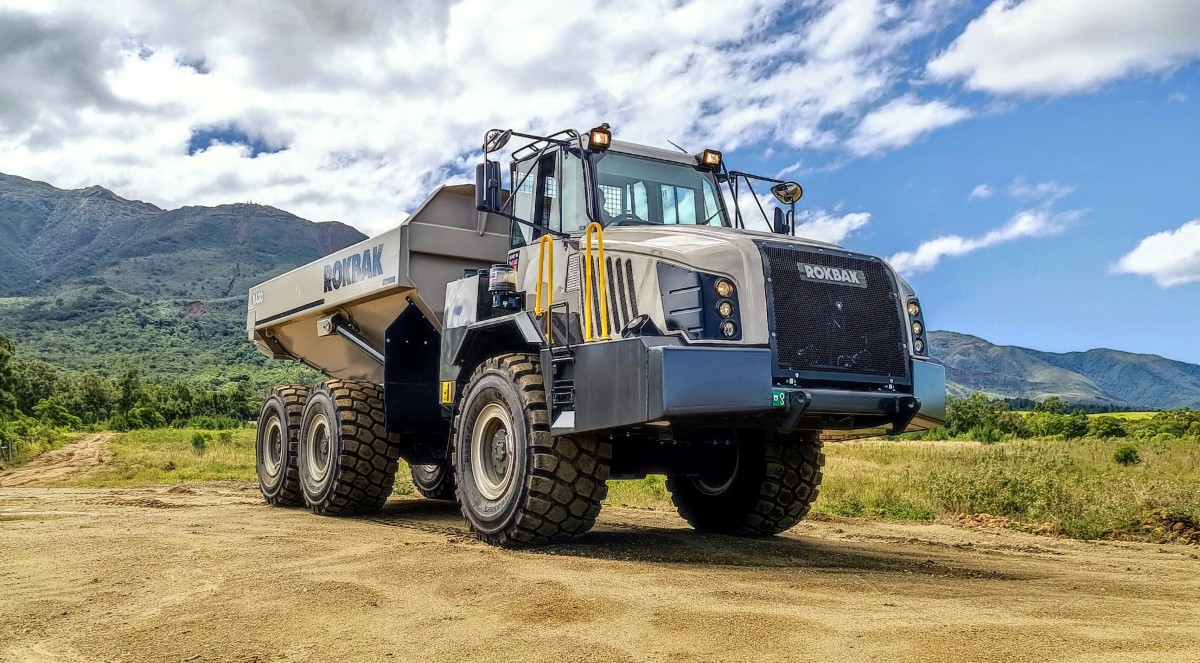
Tadano AC 7.450-1 Performs Double Duty in Wisconsin
A cost-saving and versatile solution was already on site - a...

Lifting
11/11/2024
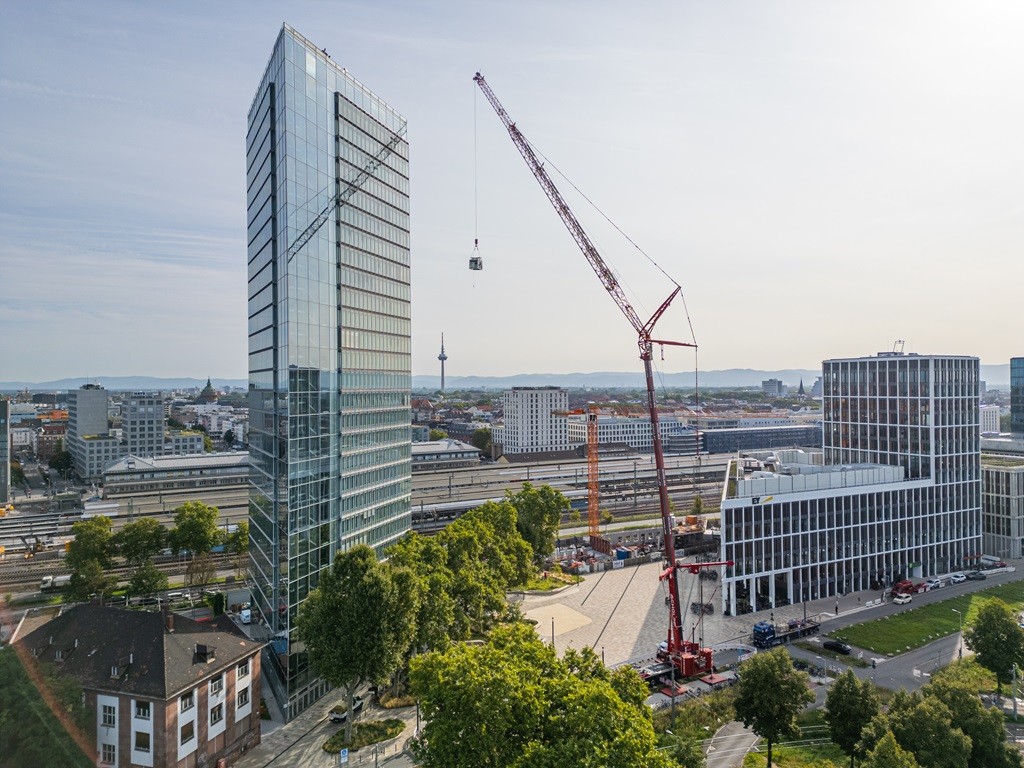
Tadano AC 7.450-1 all terrain crane for the Victoria Tower in Mannheim
Tadano AC 7.450-1 all terrain crane lifts cooling unit to to...
Altri International

International
25/11/2024
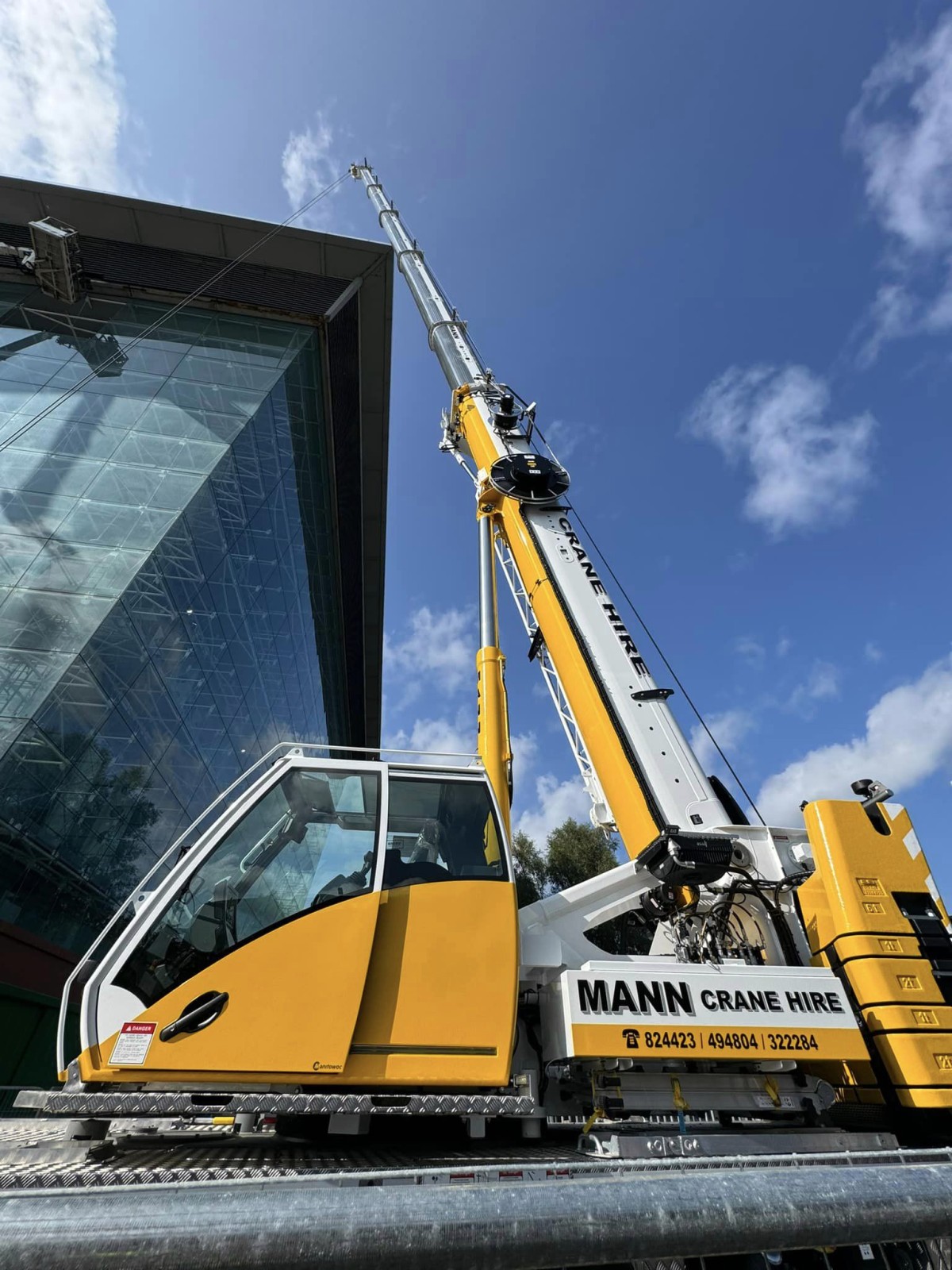
New Grove GMK3060L-1 drives busy schedule for Mann Crane Hire
• Mann Crane Hire selected the GMK3060L-1 for its class-lead...

International
25/11/2024
Prinoth Unveils Expanded Production Facility in Granby, Canada
Prinoth held an event to announce the official opening of it...

International
23/11/2024
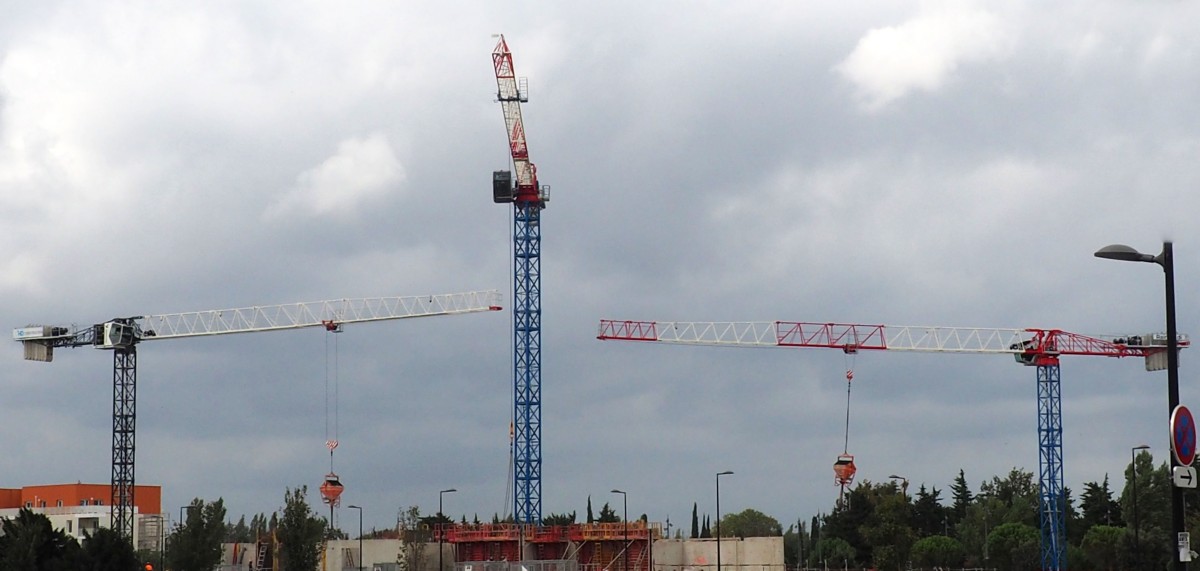
GPMat International takes delivery of two Raimondi T147s residential development in the South of France
- Official agent of France expands its product lineup with t...

International
22/11/2024
Sarens acquires additional SCHEUERLE SPMT K24 modules
renowned for its expertise in crane rental services, heavy l...
International
22/11/2024
Five WOLFF cranes modernize Oslo’s Ulven district
With a total of five WOLFF cranes of type 7534.16 Clear, Wol...

International
21/11/2024
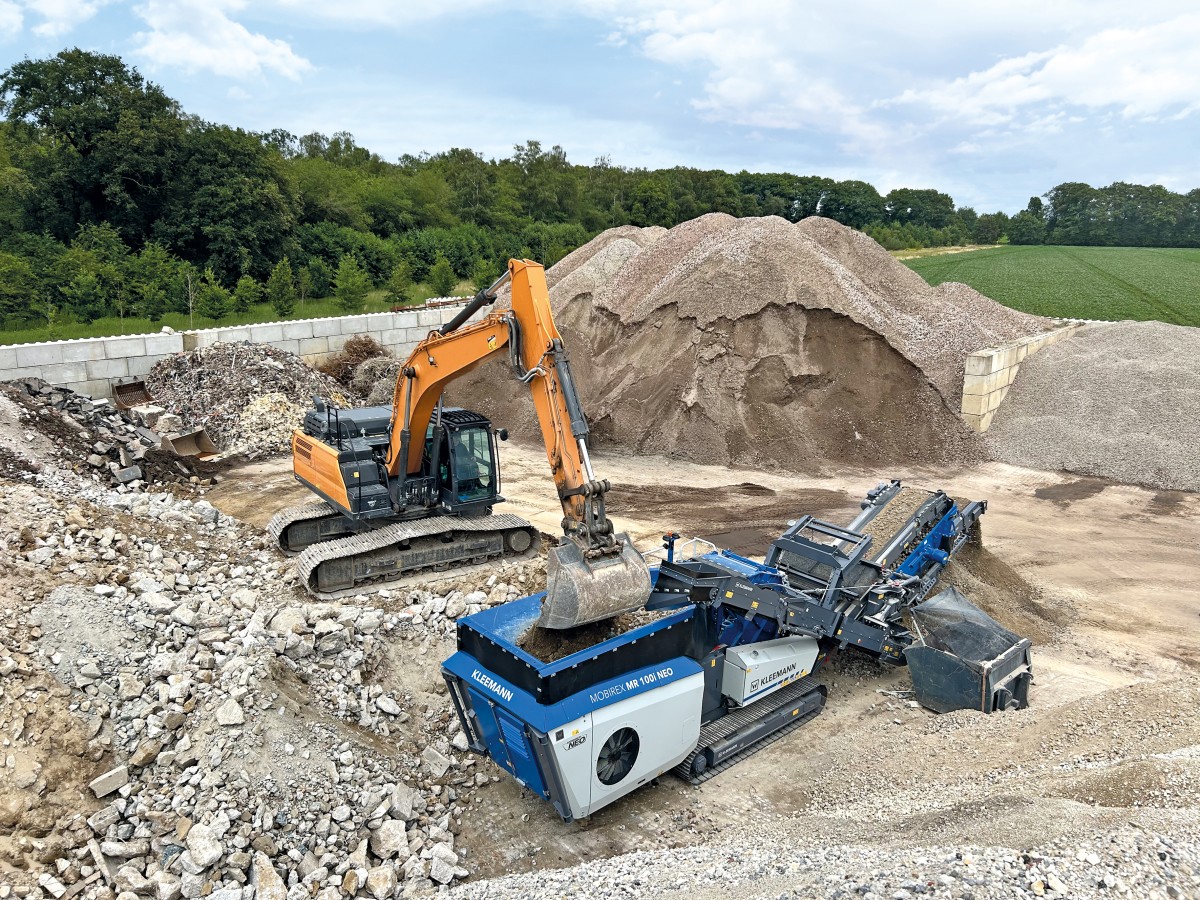
Kleemann: New compact crusher used for recycling
Impact crusher MOBIREX MR 100i NEO impresses during operatio...